Annals of Pharmacotherapy, Ahead of Print.
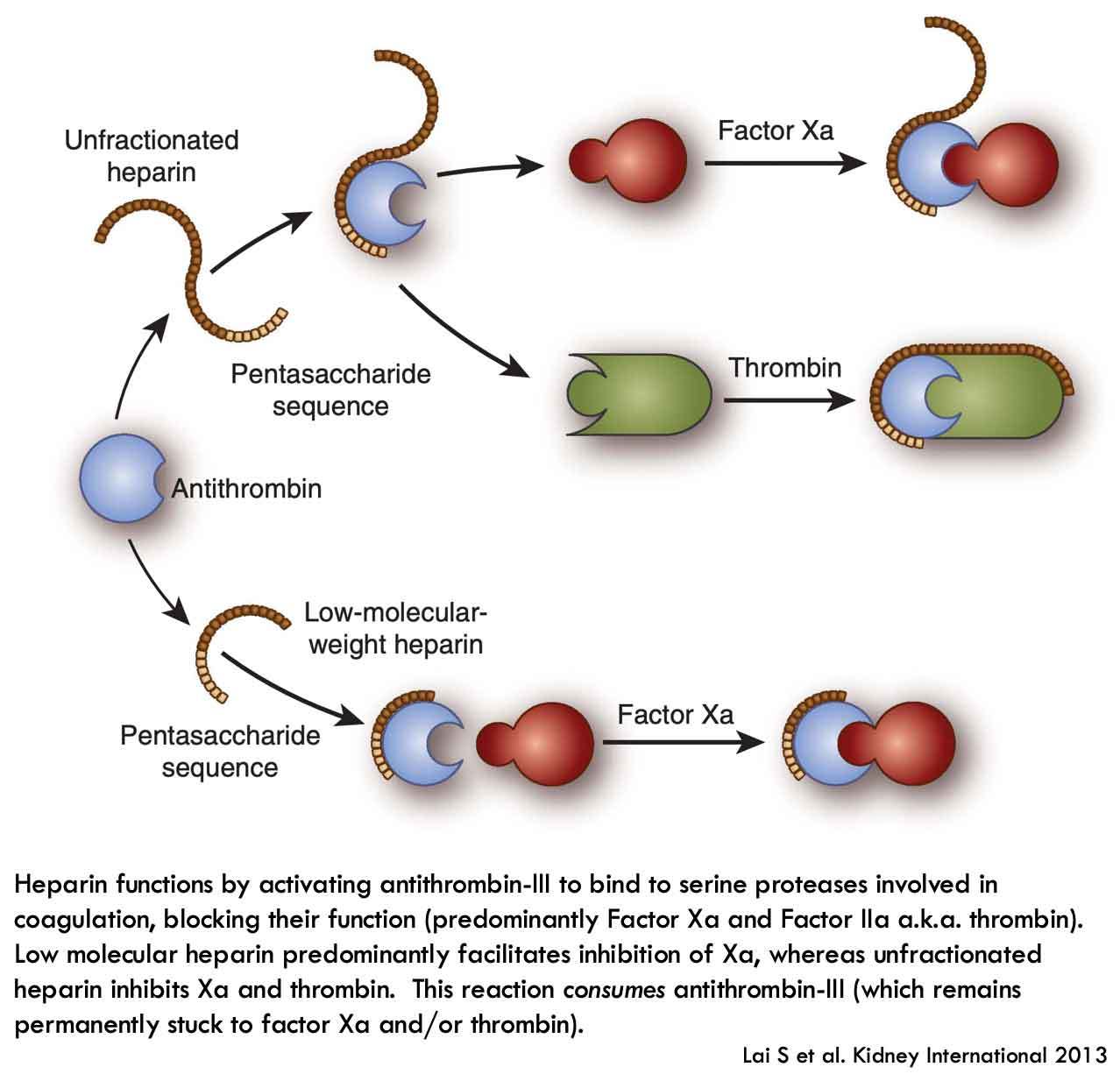
Background: Fixed-dose 2.5 mg of fondaparinux subcutaneous injection once daily has been recommended in treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) irrespective of body weight (BW). However, data on anti–factor Xa (anti-FXa) activity of fondaparinux are scarce in low-BW patients. Objective: We aimed to assess anti-FXa activity of fondaparinux in low-BW patients (BW < 50 kg) compared with normal-BW patients (BW ≥ 50 kg) who presented with NSTE-ACS. Methods: This is a prospective cohort study of patients with NSTE-ACS receiving fondaparinux. Anti-FXa activity was measured 4 hours after 2.5 mg subcutaneous injection of fondaparinux after the first 2 doses. Results: Among 87 enrolled patients, 18 (21%) had BW <50 kg. Patients in the low-BW group were older and had lower creatinine clearance. Median duration of fondaparinux therapy was 3 (IQR 2-4) days. Anti-FXa activity after the first dose of fondaparinux was similar between the low-BW and normal-BW groups (0.40 ± 0.15 vs 0.40 ± 0.17 mg/L, P = 0.914). However, anti-FXa activity after the second dose of fondaparinux was significantly higher in the low-BW group as compared with the normal-BW group (0.53 ± 0.10 vs 0.44 ± 0.16 mg/L, P = 0.011). Multivariate analysis showed that BW was the only independent factor that inversely correlated with anti-FXa activity. There was only 1 bleeding event during hospitalization in the normal-BW group and none in the low-BW group. Conclusion and Relevance: Anti-FXa activity of the second dose of fondaparinux was higher in low-BW patients but still within the expected range.
Background: Fixed-dose 2.5 mg of fondaparinux subcutaneous injection once daily has been recommended in treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) irrespective of body weight (BW). However, data on anti–factor Xa (anti-FXa) activity of fondaparinux are scarce in low-BW patients. Objective: We aimed to assess anti-FXa activity of fondaparinux in low-BW patients (BW < 50 kg) compared with normal-BW patients (BW ≥ 50 kg) who presented with NSTE-ACS. Methods: This is a prospective cohort study of patients with NSTE-ACS receiving fondaparinux. Anti-FXa activity was measured 4 hours after 2.5 mg subcutaneous injection of fondaparinux after the first 2 doses. Results: Among 87 enrolled patients, 18 (21%) had BW <50 kg. Patients in the low-BW group were older and had lower creatinine clearance. Median duration of fondaparinux therapy was 3 (IQR 2-4) days. Anti-FXa activity after the first dose of fondaparinux was similar between the low-BW and normal-BW groups (0.40 ± 0.15 vs 0.40 ± 0.17 mg/L, P = 0.914). However, anti-FXa activity after the second dose of fondaparinux was significantly higher in the low-BW group as compared with the normal-BW group (0.53 ± 0.10 vs 0.44 ± 0.16 mg/L, P = 0.011). Multivariate analysis showed that BW was the only independent factor that inversely correlated with anti-FXa activity. There was only 1 bleeding event during hospitalization in the normal-BW group and none in the low-BW group. Conclusion and Relevance: Anti-FXa activity of the second dose of fondaparinux was higher in low-BW patients but still within the expected range.