What You Should Know:
Researchers at NYU Langone Health, the academic medical center of New York University, have collaborated with NVIDIA experts to develop a large language model (LLM) that predicts a patient’s risk of 30-day readmission, as well as other clinical outcomes.
The LLM was deployed in the healthcare system’s six inpatient facilities, the NYUTron model — featured today in the scientific journal Nature that will provide doctors with AI-driven insights that could help them identify patients in need of a clinical intervention to reduce the likelihood of readmission.
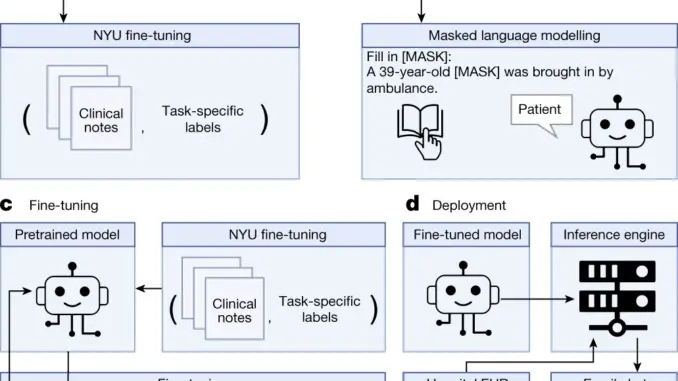
How NYUTron Works
NYUTron is an LLM with hundreds of millions of parameters, trained using the NVIDIA NeMo Megatron framework on a large cluster of NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs. NYUTron was pretrained on 10 years of health records from NYU Langone Health: more than 4 billion words of clinical notes representing nearly 400,000 patients. The model achieved an accuracy improvement of more than 10 percent over a state-of-the-art machine learning model to predict readmission. Once the LLM was trained for the initial use case of 30-day readmission, the team was able to spin out four other predictive algorithms in around a week. These include predicting the length of a patient’s hospital stay, the likelihood of in-hospital mortality, and the chances of a patient’s insurance claims being denied.
“When you discharge a patient from the hospital, you don’t expect them to need to return, or you probably should have kept them in the hospital longer,” said Dr. Eric Oermann, assistant professor of radiology and neurosurgery at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and a lead collaborator on NYUTron. “Using analysis from the AI model, we could soon empower clinicians to prevent or fix situations that put patients at a higher risk of readmission.”
To date, the model has so far been applied to more than 50,000 patient discharged in NYU’s healthcare system, where it shares predictions of readmission risk with physicians via email notifications. Oermann’s team is next planning a clinical trial to test whether interventions based on NYUTron’s analyses reduce readmission rates.