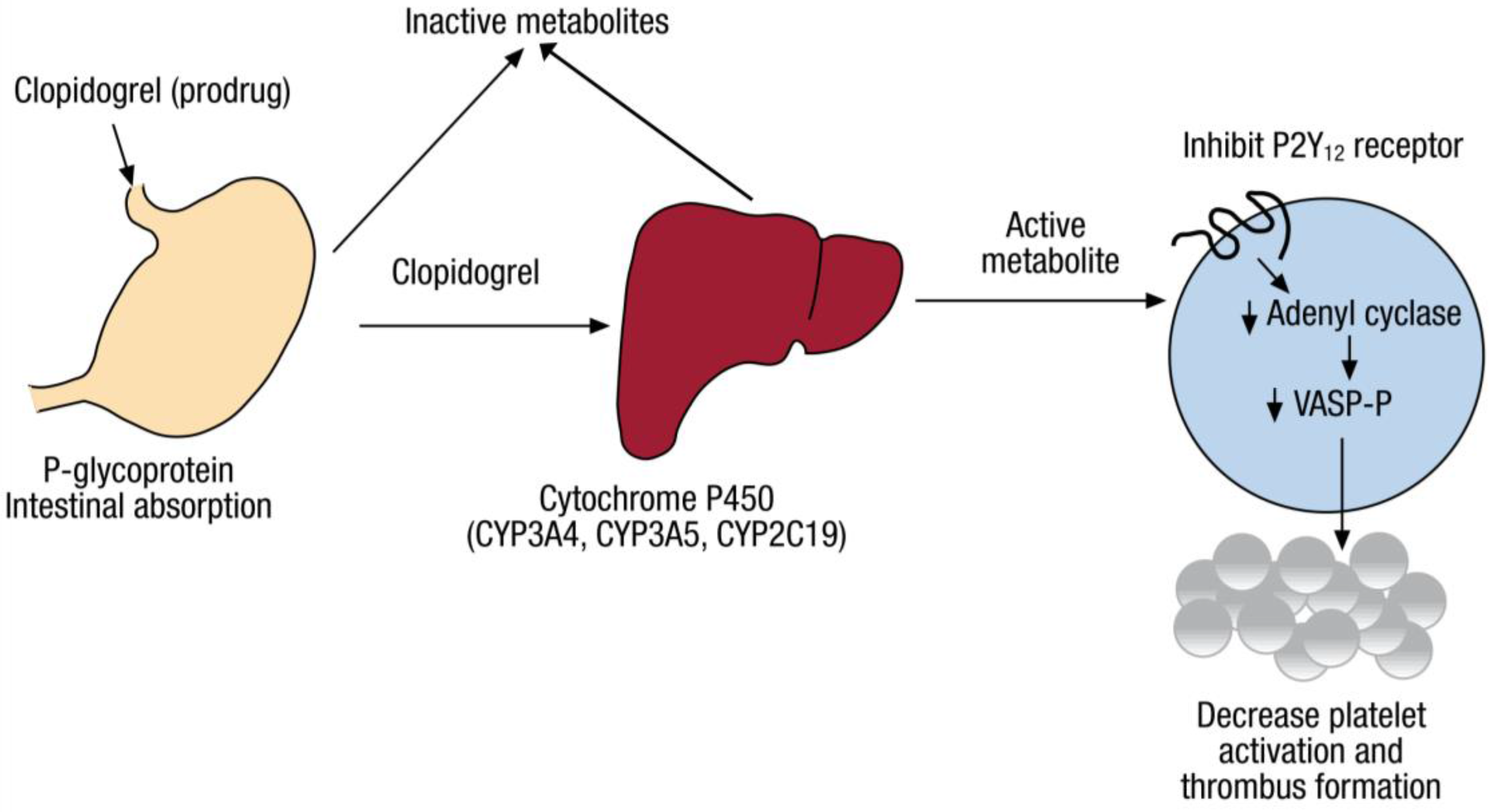
Clopidogrel, the top prescribed antiplatelet medication for individuals who have experienced a myocardial infarction or cerebral vascular accident or who have peripheral arterial disease, is administered orally as a prodrug. It relies on hepatic metabolism through cytochrome P450 enzymes for conversion to its active form. Current research shows that allelic variation m the gene coding for CYP2C19 is the main factor contributing to the variability of response associated with clopidogrel treatment. Through the promotion of genetic testing for variability in the CYP2C19 gene and competently interpreting test results, pharmacists have the opportunity to use these findings to significantly impact clopidogrel prescribing and dosing. By tailoring an individual’s dosing regimen, pharmacists can maximize the efficacy of clopidogrel for a patient according to his or her genotype.
