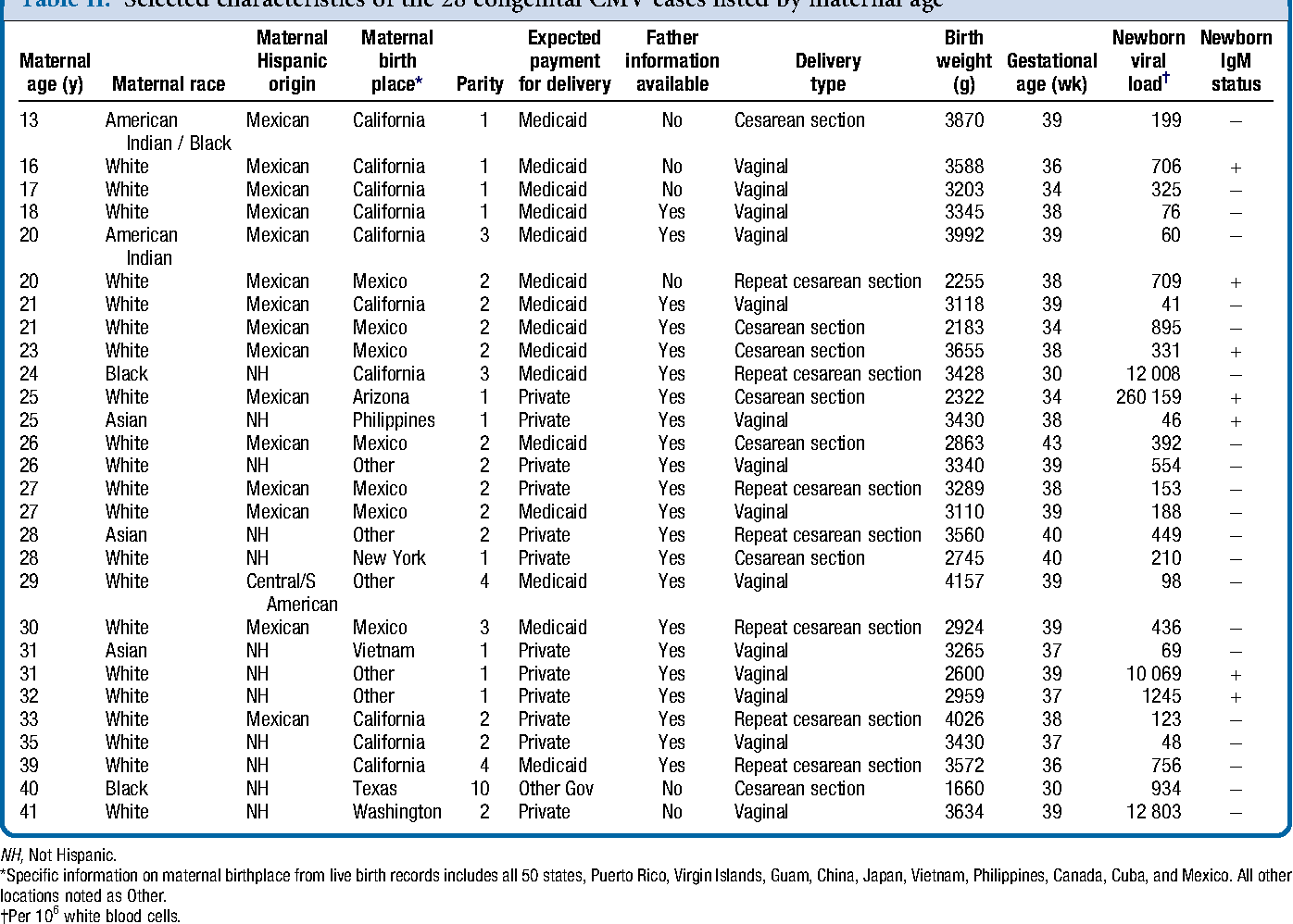
Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) is the most common virus spread in utero from mother to fetus, leading to more long-term problems and childhood deaths than other conditions such as Down syndrome, fetal alcohol syndrome, pediatric HIV/AIDS, or neural tube defects. The majority of congenital CMV infections are primary infections in which the mother acquires the infection during pregnancy. Current treatment options for CMV infection are available, but there is limited data on safety and effectiveness in pregnant mothers and neonates. Prevention by screening for CMV is associated with a high cost, and vaccines are currently unavailable. Studies show that education and behavioral modifications are effective ways to lower the risk of CMV infection in neonates, making primary prevention by these methods critical to reducing the transmission of CMV infection.
