cbaker_admin
Thu, 08/27/2020 – 10:00
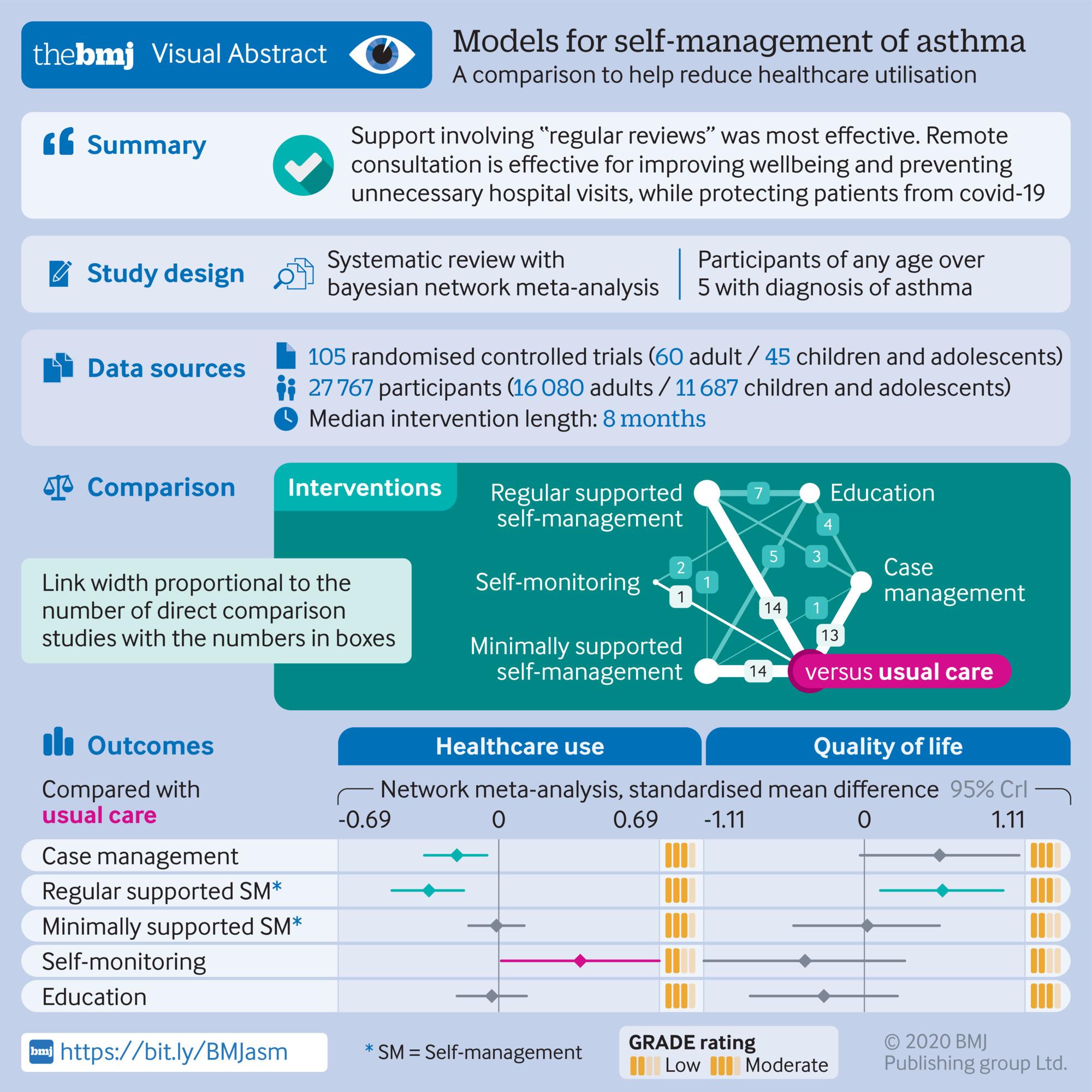
A U.K. systematic review and network meta-analysis assessed the value of self-management interventions in achieving better quality of life and lowering health care utilization among people with asthma. Researchers combed the literature for relevant studies on the various self-management models, including multidisciplinary case management, regularly supported self-management, and minimally supported self-management. They ultimately included 105 randomized controlled trials with more than 27,750 participants. Analysis revealed that regularly supported self-management was the only approach that was significantly better than standard care and education for both reducing hospital admissions or emergency department visits and enhancing quality of life. The technique also was the only one yielding benefit in trials involving children and adolescents. Going forward, the review authors recommend that asthma patients should receive no less than 2 hours of coaching in self-management skills, with multidisciplinary case management reserved for those with severe disease.
