Over the years, the incidence and prevalence of chronic diseases, have increased significantly. Presently, the recommended treatment options for such clinical conditions are mostly biologics, which need to be administered via parenteral routes to ensure maximum therapeutic benefit. Given the inherent requirement for frequent medication, patients suffering from such long-lasting clinical conditions generally end up spending high amounts on the prescribed therapeutic regimen, and numerous hospital visits for dose administration. However, several drug delivery devices that enable patients to self-administer their respective medications are now available. Over time, the growing adoption of such devices has a significant impact on patients suffering from chronic illnesses. This is primarily because of their ease-of-use and cost effectiveness, in terms of allowing consumers to avoid expensive visits to hospitals / outpatient clinics. Biologics have emerged as a direct consequence of the rapid development that has taken place in the field of life sciences, particularly in cell and molecular biology, over the past few decades. There are a variety of biologically derived therapeutics that are presently available / being developed. Examples of some of the most popular types of biologically derived therapeutics have been depicted below.
Subcutaneous biologics – current market landscape
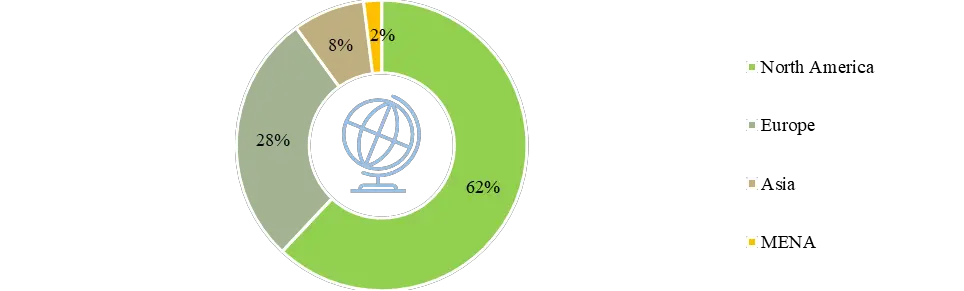
Currently, more than 190 players are engaged in the development / distribution of subcutaneous biologics across the globe. Of these, 50 players have approved subcutaneous biologics. Although players that provide approved subcutaneous biologics are present across the globe, most of them are headquartered in North America, followed by Europe. Pasted below is a donut chart, showing the regional distribution of companies offering approved subcutaneous biologics.
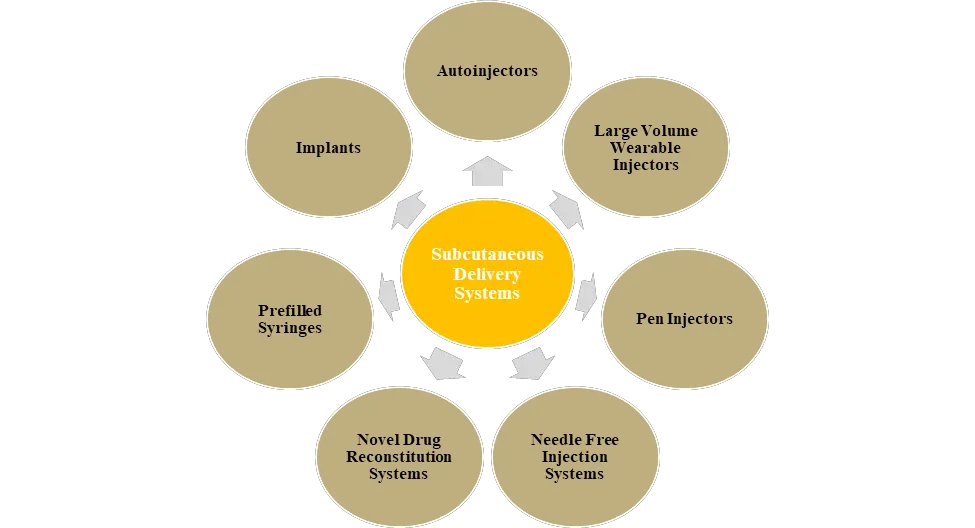
Subcutaneous drug delivery systems – the helping hand for patients
There has been a significant increase in the number of biologics, specifically the new generation molecules, such as monoclonal antibodies, in the late-stage clinical studies (phase II / phase III). Many of these antibody-based products are highly viscous and need to be administered using delivery systems in volumes that exceed the standard fill of a 1 mL prefilled syringe. Medical device manufacturers have developed a diverse range of products that can enable subcutaneous delivery of various injectable therapies. Several devices have been combined with the drugs to form drug-device combination products to be directly used by the patients and many are under development. Over the past few years, the pharmaceutical industry has witnessed significant advances and innovation in the field of drug delivery systems. The emergence of safer and patient-friendly devices is acting as a strong enabler for subcutaneous delivery of therapeutics. Examples of some of the most popular types of drug delivery systems have been depicted below.
Future opportunities for subcutaneous biologics and their delivery systems
The subcutaneous method of drug delivery is an emerging field, which is deemed to possess significant future potential. It offers a number of advantages over conventional methods of drug delivery (oral and parental). Hence, given the fact that several biologics have been approved for the treatment of a range of clinical conditions, coupled with a strong clinical pipeline, the domain is expected to offer high potential opportunities in the coming years. Further, subcutaneous drug delivery devices, such as wearable infusion pumps, autoinjectors, pen injectors, microneedles, needle free injectors and large volume injectors, have, of late, gained significant attention within the pharma industry. This can be attributed to their relatively more efficient and patient friendly mode of drug delivery. These devices can be used for controlled delivery of small molecules, as well as large macromolecules (such as insulin, growth hormones, immunobiological vaccine, receptor agonist, proteins and peptides). In fact, there are advanced delivery devices which can deliver highly viscous and concentrated formulations and doses, as high as 50 ml, via the subcutaneous route. Therefore, the market is expected to provide lucrative opportunities for developers that are currently engaged in the development / distribution of drug delivery systems.
For more details on this emerging domain, check out the following report:
Subcutaneous Biologics, Technologies and Drug Delivery Systems Market
You may also be interested in the following titles:
- Continuous Manufacturing (Small Molecules and Biologics) Market
- Subcutaneous Biologics, Technologies and Drug Delivery Systems Market
- Antibody Discovery Services and Platforms Market
Our Social Media Platform
Web: https://www.rootsanalysis.com/
LinkedIn: https://in.linkedin.com/company/roots-analysis
Twitter: https://twitter.com/RootsAnalysis.com
The post Subcutaneous Biologics: The Unmet Requirement in the Pharmaceutical Space appeared first on Blog.
